Oral Candidiasis In Children – You Are Mom

First of all, oral candidiasis in children is also called oral thrush or oral yeast infection. It is a common opportunistic infection of the oral cavity.
It results from an overgrowth of fungi of the Candida species, the most common being Candida Albicans. In addition, the incidence varies depending on age and certain predisposing factors. It most often affects infants under 6 months and newborns.
Causes of oral candidiasis in children
Certain microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, etc.) regularly live in the body. Some are harmless, but others can trigger an infection.
Since the immune system of children and infants is not fully developed, they are more prone to infections. It is fungi that regularly live in the body that cause these infections. The risk factors include the following:
- impaired function of the salivary glands.
- medications (certain antibiotics or corticosteroids)
- dental prostheses
- a diet rich in carbohydrates and extreme life situations, but also
- smoking
- diabetes mellitus
- Cushing’s syndrome.
- Malignant neoplasms, but also
- Immunosuppressive disorders in the elderly and newborns.
Classification of candidiasis
Sometimes the yeast Candida Albicans grows and overgrows in the oral cavity. In this case, these lesions are called “canker sores”. According to studies published in Dermatologic therapy, oral candidiasis can be classified according to their course or location:
- Acute candidiasis : it is subdivided into its pseudomembranous and erythematous forms.
- Chronic candidiasis : pseudomembranous, erythematous (atrophic) and hyperplastic forms.
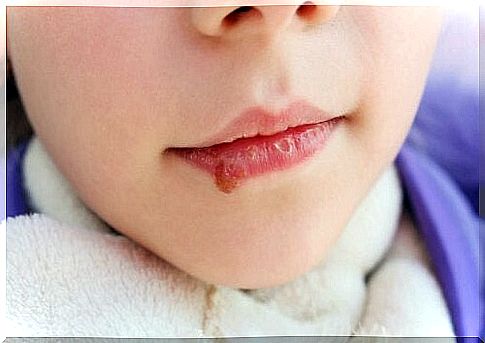
- Angular cheilitis: also called infectious angular cheilitis. These are cold sores at the corners of the lips.
Symptoms and signs of oral thrush
The clinical picture triggered by a Candida yeast infection may be similar to that of other health problems. Symptoms of thrush include the following:
- Odynophagia (sore throat).
- Dysphagia (pain on swallowing).
- Halitosis or loss of taste and appetite.
- Bleeding due to rubbing lesions, but also
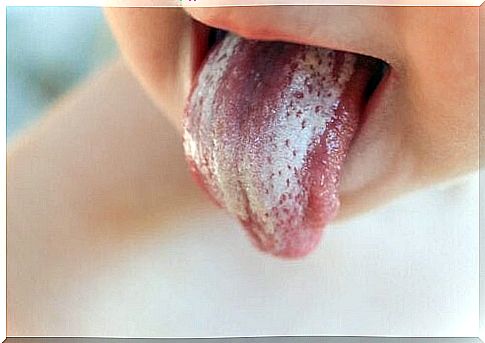
- White, silky lesions on the tongue and in the mouth.
However, there are usually no symptoms of discomfort or general severity. In some cases, there are not even symptoms and the lesions are painless.
Diagnosis of candidiasis in children
The diagnosis of candidiasis in children is made in consultation with the specialist doctor. This is where the professional will interview the child or mother to study any predisposing factors and medical history. Finally, the clinical results in the patient will complete the interrogation carried out. They will both help to establish an accurate diagnosis.
In cases where there are some doubts when establishing and defining a diagnosis, a sample of the lesion is taken. This sample allows the lesion to be analyzed under a microscope in the laboratory. There are even more serious cases in which the candidiasis spreads to areas of the esophagus. Therefore, a culture of the affected tissue should be done to study the microbe that produced it.
What are the treatment options?
An important part of the treatment of candidiasis in children is to do the correct mouthwash. In other words, healthy patients will recover more easily than those with an underlying condition.
Antifungals are drugs used to treat candidiasis. In addition, the type of antifungal to choose will depend on the location of the lesion in the body (nystatin, clotrimazole, fluconazole, miconazole, amphotericin B).
In mild cases of oral thrush in children, it is recommended to take medication prescribed by the doctor, whether tablets, tablets or capsules.
In addition, children are advised to consume yogurt or ingest probiotics such as Lactobacillus which reduce the growth of Candida Albicans. In addition, they prevent infections, according to published studies on yeast infection.
Tips for preventing future candidiasis outbreaks
There is a high likelihood of future candidiasis if the cause has not been treated properly and effectively. This is why the best way to treat oral thrush and prevent recurrent infections is to tackle the underlying cause.
Some of the following recommendations help to avoid new episodes in the future:
- Maintain good oral hygiene : do not share toothbrushes and replace them often enough. Indeed, it is essential to have good oral hygiene every day.
- Disinfect utensils : disinfect bottles, pacifiers but also utensils that are commonly used by infants and children.
- Mouthwash : Perform mouthwash to keep the oral cavity clean. One option is to rinse your mouth with lukewarm salt water.
Prognosis of oral thrush in children
Eventually, candidiasis in children can develop without symptoms or signs. However, when the lesions are present and treatment is started, it usually resolves within two weeks. However, in children with weakened immune systems, the treatment process takes longer and requires more care.









